This article focuses on system precision and local accuracy, as tested in an office environment. For results on global accuracy and georeferenced accuracy from a large warehouse, please refer to our previous white paper. Note: The first two sections of this article (the Introduction and Why We Performed These Tests) are identical to those in the previously mentioned white paper. If you've already read that document, we recommend starting from the Defining Our Terms section below. Pipe Supports,Steel Pipe Supports,Slide Pipe Supports,Brass Pipe Slide Bar Simcan Industrial Equipment Co.,Ltd. , https://www.simcanindustry.comTEST RESULTS OVERVIEW
Introduction
In recent years, LiDAR has become one of the most trusted technologies for creating accurate and detailed 3D models. Industries such as mining, construction, and infrastructure use these models for inspections, safety assessments, asset tracking, and project planning.
The outputs from 3D models built with LiDAR include digital twins, precise 2D/3D measurements, defect identification, and the ability to export data in common formats like *.e57, *.las, *.laz, and *.ply. Merging multiple georeferenced models also allows for tracking changes over time.
Regardless of the industry or application, the quality of the 3D model is crucial. If the data lacks precision and accuracy—terms with specific meanings in 3D modeling—the model may not reflect reality accurately enough to be useful.
This article presents findings from tests conducted by GeoSLAM and Flyability teams, focusing on the system precision and local accuracy of 3D models created using the Elios 3 with GeoSLAM Connect, compared to leading mobile mapping systems like the ZEB Revo and ZEB Horizon.
Why We Performed These Tests
Flyability’s Elios 3 features an Ouster OS0-32 LiDAR sensor and SLAM capabilities, allowing it to generate real-time 3D models during flight. After the mission, users can process the LiDAR data with GeoSLAM Connect to create high-quality 3D models.
The 3D Live Model is used during missions for navigation and route planning, while the post-processed model provides a precise point cloud. Processing Elios 3 data with GeoSLAM Connect enhances its collision-tolerant design, making it ideal for mapping confined spaces.
However, potential users may wonder about the impact of drone vibrations or environmental factors like dust and moisture on the final 3D models. To address these concerns, we conducted a thorough assessment of system precision and local accuracy using the Elios 3 with GeoSLAM Connect. All tests were designed to be representative and repeatable.
Defining Our Terms: Precision and Local Accuracy in 3D Mapping
When discussing 3D models made with LiDAR data, the terms precision and accuracy have distinct meanings.
Accuracy refers to how close a measured value is to the true or benchmark value. For example, if a point cloud measures 100mm but the actual distance is 500mm, the measurement is inaccurate.
Local accuracy relates to the distance between points in a single view, such as the dimensions of a room. This article focuses only on local accuracy for the Elios 3 and GeoSLAM Connect.
Precision refers to the consistency of repeated measurements. If five measurements of the same distance yield the same result, the data is precise. Precision is often linked to noise or repeatability.
The required level of precision depends on the industry. Mining may accept centimeter-level precision, while construction may require higher accuracy.
It's important to note that low precision increases noise in the point cloud, making feature detection more challenging.
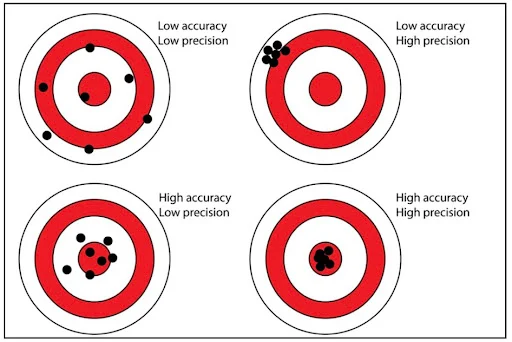 Accurate measurements fall in the bullseye. Precise measurements are tightly clustered.
Accurate measurements fall in the bullseye. Precise measurements are tightly clustered.System Precision and Local Accuracy Assessments with the Elios 3
To evaluate the precision and local accuracy of the Elios 3 with GeoSLAM Connect, GeoSLAM experts and Flyability engineers conducted:
- A Plane-to-Plane analysis to test local accuracy
- A Range Noise evaluation to assess system precision
Establishing a Control
For any accuracy test, a more accurate reference system is needed. In this case, a Riegl VZ-400 TLS served as the control, with an accuracy of 5mm at 1-sigma.
Collecting the Data
Both the Elios 3 and the Riegl VZ-400 captured data in an indoor environment. The TLS provided the reference model, which was then used to validate the Elios 3 data.
Aligning the Elios 3 Point Cloud to the Reference Model
The Elios 3 point cloud was aligned to the TLS reference model using PolyWorks|Inspector MRS2019 IR3 software. This involved manual alignment followed by an automated Best-Fit algorithm to minimize deviations.
Assessing Local Accuracy—Plane-to-Plane Comparison
A Plane-to-Plane comparison was performed by fitting planes to both the Elios 3 data and the reference model. The Normal Distance between the planes was calculated to assess local accuracy.
Assessing System Precision—Range Noise Analysis
Range Noise was calculated by measuring the deviation of each point from the mean range in selected planar surfaces. The results showed a Mean Standard Deviation of 8mm to 1-sigma.
Test Environment
The tests were conducted in a standard office space with six planar surfaces, each approximately 1 meter square. The test setup ensured consistent conditions for accurate comparisons.
System Precision and Local Accuracy Test Results
Here are the results of the local accuracy and precision tests.
Assessing Local Accuracy
Using Plane-to-Plane analysis, the Elios 3 demonstrated a mean Normal Distance of 8mm (.32 inches) from the reference model, with all values within ±16mm.
Assessing System Precision
The Range Noise analysis revealed a Mean Standard Deviation of 8mm to 1-sigma, indicating high system precision.
Conclusion
The Elios 3 with GeoSLAM Connect produced 3D models with excellent local accuracy and precision, comparable to traditional TLS systems and leading mobile mapping solutions. These results confirm the reliability of the Elios 3 for professional applications in various industries.
Testing Local Accuracy and System Precision in 3D Mapping with the Elios 3 and GeoSLAM Connect
